Tour Operator CRM A Comprehensive Guide
Tour operator CRM systems are essential tools for modern tour operators, streamlining operations and enhancing customer relationships. This guide dives deep into the intricacies of these powerful platforms, examining their core functionalities and how they can be leveraged to maximize efficiency and profitability. From lead generation to personalized recommendations, we’ll explore how a well-implemented CRM can transform a tour operator’s business.
This comprehensive guide will cover everything from defining a tour operator CRM and its key differences from general CRM software, to the process of integration with other business systems. We will also delve into implementation strategies, maintenance best practices, and the specifics of addressing diverse tour operator needs, including those of small businesses and large corporations. Finally, we’ll explore data management, reporting, and the critical role of data analysis in driving strategic business decisions.
Defining Tour Operator CRM
A Tour Operator CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system is a specialized software designed to streamline and manage the entire customer journey for tour operators. It encompasses functionalities for handling customer interactions, managing bookings, tracking itineraries, and analyzing data to enhance operational efficiency and boost profitability. This system allows tour operators to centralize customer information, automate tasks, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
This specialized CRM system differs significantly from a general CRM. While general CRMs might focus on broader business relationships, a tour operator CRM has tailored features for managing travel-specific elements such as itineraries, booking details, and payment processes. This allows for a more focused and effective management of travel-related operations.
Types of Tour Operator CRMs
Various deployment models cater to different needs and budgets. Cloud-based CRMs offer accessibility and scalability, while on-premise solutions provide more control over data storage and customization. Choosing the right deployment model is crucial for optimal functionality and long-term success. Other options might include hybrid solutions that combine elements of both cloud and on-premise models.
Examples of Tour Operator CRM Systems
Several reputable CRM systems are commonly utilized by tour operators. Examples include [CRM System 1], [CRM System 2], and [CRM System 3]. Each system offers specific features catering to the unique needs of tour operators, ranging from simple booking management to sophisticated data analysis tools. The choice of system often depends on the size and complexity of the tour operator’s business.
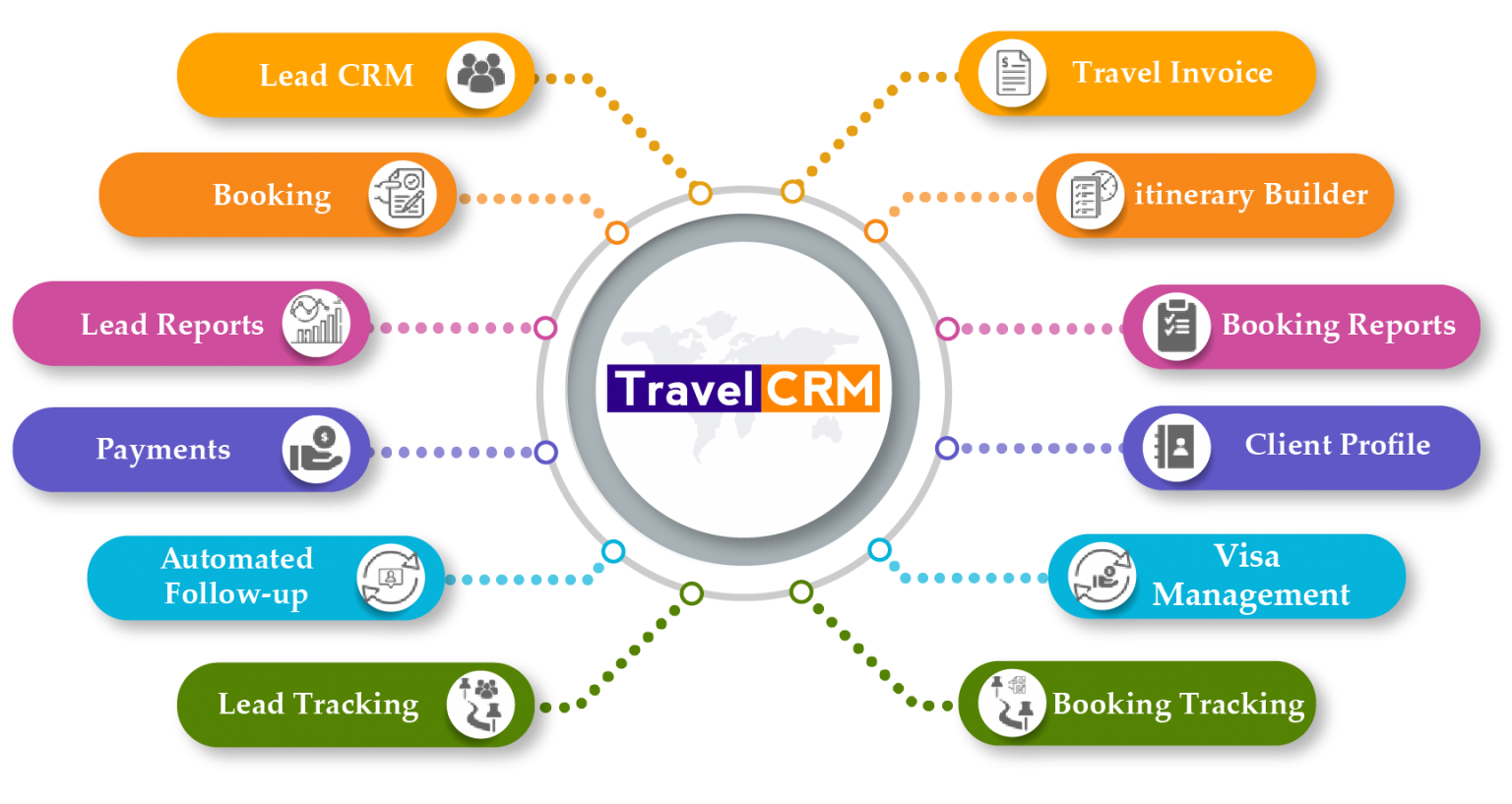
Key Features and Benefits of a Tour Operator CRM
A Tour Operator CRM provides a comprehensive suite of tools to enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. The following table highlights key features and their associated benefits:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Customer Relationship Management | Centralized customer data for improved communication and service personalization. |
| Booking Management | Streamlined booking process, reducing errors and improving efficiency. |
| Itinerary Management | Easy creation, modification, and tracking of tour itineraries. |
| Payment Processing | Secure and efficient handling of payments, including online transactions. |
| Reporting and Analytics | Data-driven insights into business performance and customer behavior. |
| Marketing Automation | Targeted marketing campaigns and improved customer engagement. |
| Inventory Management | Effective tracking of available resources, such as hotel rooms and transportation. |
| Scalability | Adaptability to accommodate business growth and expansion. |
CRM Functionality for Tour Operators
A robust Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is crucial for tour operators to effectively manage their customer interactions and business operations. A well-implemented CRM system streamlines processes, enhances customer experiences, and fosters lasting relationships, ultimately driving profitability and growth.
Role of a CRM in Managing Customer Relationships
A CRM system acts as a central repository for all customer data, including contact information, booking history, preferences, and communication details. This centralized approach allows tour operators to maintain a complete and accurate view of each customer, enabling personalized interactions and tailored service offerings. This holistic understanding of customers empowers tour operators to anticipate needs, proactively address concerns, and build stronger, more meaningful relationships.
Lead Generation and Qualification
A CRM system plays a pivotal role in lead generation by enabling operators to track potential customers, qualify leads based on specific criteria, and nurture them effectively. By automating lead capture through online forms, website interactions, and marketing campaigns, tour operators can efficiently manage a large volume of leads. Detailed lead profiles enable better targeting and personalized communication strategies. This process effectively identifies high-potential leads, increasing the conversion rate from lead to customer.
Streamlining the Booking Process
CRMs streamline the booking process by automating various stages, from initial inquiry to final confirmation. Automated responses to inquiries, pre-filled forms for booking details, and integrated payment gateways reduce manual effort and improve efficiency. This automation enhances the overall booking experience for customers, improving satisfaction and reducing delays. This ultimately contributes to improved customer satisfaction.
Managing Customer Communications
CRMs facilitate effective communication management through various channels. Automated email sequences, personalized SMS messages, and push notifications allow tour operators to maintain consistent contact with customers throughout the entire journey. This proactive communication enhances customer engagement and builds trust, keeping customers informed about important updates and offers.
Tracking Customer Preferences and History for Personalized Recommendations
CRMs enable the tracking of customer preferences and past travel history. This data allows for the creation of personalized recommendations, tailoring future offers and services to individual customer needs. By analyzing past bookings and preferences, operators can suggest relevant tours, packages, and add-ons, enhancing customer satisfaction and encouraging repeat business.
Impact of CRM Functionalities on Tour Operator Business
| CRM Functionality | Impact on Tour Operator Business |
|---|---|
| Lead Generation & Qualification | Increased lead conversion, improved sales, better targeting |
| Booking Process Automation | Reduced manual effort, improved efficiency, faster response times |
| Customer Communication Management | Enhanced customer engagement, improved communication, and increased customer satisfaction |
| Personalized Recommendations | Increased customer satisfaction, repeat business, improved customer lifetime value |
| Centralized Customer Data | Improved customer service, better understanding of customer needs, enhanced personalization |
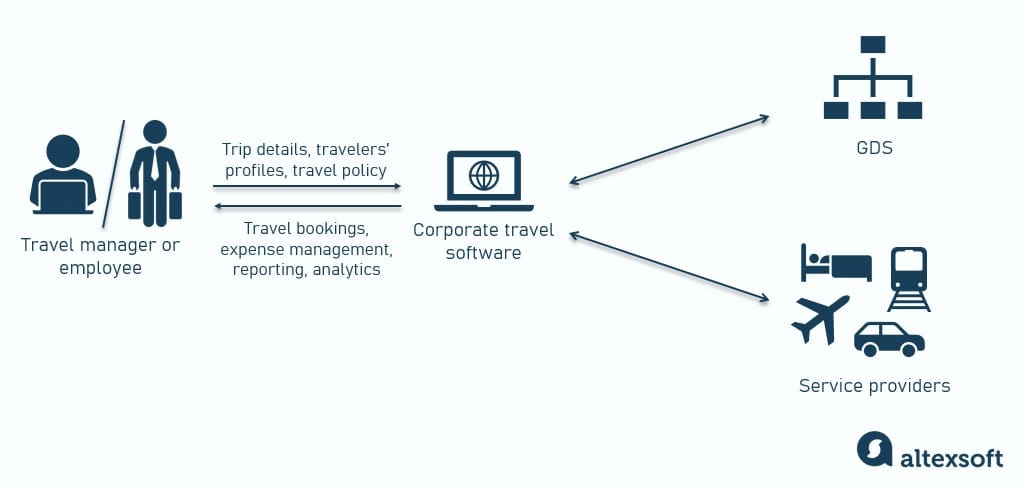
Integrating CRM with Other Systems
A robust Tour Operator CRM isn’t an isolated system; its true power lies in its ability to seamlessly integrate with other crucial business functions. Integrating with accounting, inventory, and marketing automation platforms unlocks a wealth of data that fuels smarter decision-making and streamlined operations. This interconnectedness streamlines workflows, reduces manual errors, and ultimately improves the overall efficiency of the tour operator’s business.
Importance of Integration
Integrating a CRM with other business systems, such as accounting and inventory, is crucial for a tour operator’s success. This interconnectedness eliminates data silos, providing a holistic view of the business. Real-time data sharing enables accurate financial reporting, improved inventory management, and enhanced customer relationship management. Data consistency across systems minimizes errors, boosts operational efficiency, and facilitates informed decision-making.
Integration Process
The integration process typically involves a series of steps. First, a thorough assessment of the existing systems and the CRM is essential to identify compatibility issues and data mapping requirements. Second, a defined data migration strategy is critical to ensure data integrity during the transfer. Third, technical configuration and testing are necessary to validate the functionality and identify potential problems. Finally, post-implementation support and ongoing maintenance are required to ensure long-term stability and functionality.
Common Integrations for Tour Operators
Tour operators commonly integrate their CRM with accounting software for automated invoice generation, payment processing, and reconciliation. Inventory management systems are integrated to ensure real-time tracking of tour packages, ensuring accurate booking and preventing overselling. Marketing automation platforms allow for targeted campaigns and personalized customer communication.
Challenges in Integration
Potential challenges during integration include data incompatibility issues, differing data formats, and system compatibility problems. The complexity of the integration process and the cost of implementation can also pose significant obstacles. Ensuring data accuracy and consistency throughout the integration process is paramount to prevent errors and ensure smooth operation.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Seamless integration enhances operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, reducing manual data entry, and improving communication between different departments. Real-time visibility into key business metrics, like inventory levels and financial performance, enables faster decision-making. This improved efficiency translates to cost savings and increased profitability.
Potential Integration Points
| CRM System | Accounting System | Inventory System | Marketing Automation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer data (name, contact details) | Invoice details, payment information | Tour package availability, pricing | Customer segmentation, email marketing |
| Booking information | Transaction details, revenue tracking | Package details, booking history | Campaign performance tracking, lead generation |
| Customer service interactions | Expense reporting | Stock updates | Personalized communication |
CRM Implementation and Maintenance
Implementing a CRM system for a tour operator requires careful planning and execution. A well-implemented CRM can significantly improve operational efficiency, enhance customer relationships, and drive revenue growth. Conversely, a poorly implemented system can lead to wasted resources and decreased profitability. Therefore, meticulous attention to detail throughout the implementation and ongoing maintenance phases is crucial.
Effective CRM implementation is not just about installing software; it’s about integrating it seamlessly into existing workflows and fostering a culture of CRM adoption within the organization. This involves clear communication, comprehensive training, and ongoing support to ensure staff effectively utilize the system.
Implementation Steps
A structured approach to CRM implementation is essential for success. This typically involves several key steps:
- Needs Assessment and Planning: Carefully evaluating current processes and identifying areas where the CRM can improve efficiency is crucial. Defining specific goals and desired outcomes, aligning the CRM system with business objectives, and creating a realistic budget are all critical to this phase. This step also involves defining roles and responsibilities within the CRM system to ensure appropriate user access and accountability.
- System Selection and Customization: Choosing a CRM system that best fits the specific needs and budget of the tour operator is important. This includes evaluating various options, considering features, and ensuring compatibility with existing systems. Customization is also important to adapt the system to unique business requirements and workflows.
- Data Migration and Import: Migrating existing data into the new CRM system is a critical phase. This involves ensuring data accuracy and consistency. It is important to create a data migration plan that includes data validation and cleanup steps to avoid errors and ensure a smooth transition.
- User Training and Support: Comprehensive training programs should be developed to equip staff with the necessary skills to use the CRM effectively. Ongoing support should be provided to address questions and provide assistance as needed. This ensures staff feels confident using the CRM.
- Testing and Deployment: Rigorous testing of the CRM system in a controlled environment is vital to identify and resolve any issues before full deployment. This testing phase helps to ensure the system is reliable and meets the operational requirements of the tour operator.
Staff Training
Effective training is critical to CRM adoption. The training program should be tailored to the specific roles and responsibilities of each staff member. The program should cover:
- System Functionality: A detailed understanding of the various features and functions of the CRM system is essential.
- Data Entry Procedures: Training on the correct methods for inputting and managing customer data is crucial for data accuracy and consistency.
- Workflow Integration: Staff need to understand how the CRM integrates with their existing workflows and how it will improve their efficiency.
- Reporting and Analysis: Instruction on how to access and interpret reports generated by the CRM system is necessary for effective decision-making.
- Problem Solving: Addressing potential issues and providing support mechanisms during the training phase is crucial for long-term success.
Maintenance and Updates
Ongoing maintenance and updates are essential for a CRM system to remain functional and effective. Regular updates address bugs, improve system performance, and enhance security. This also includes the need for regular data backups and recovery procedures.
- System Security: Maintaining a secure CRM system is crucial to protect sensitive customer data. Implementing strong passwords, access controls, and regular security audits is vital.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Establishing a robust data backup and recovery plan is critical to minimize the risk of data loss. Regular backups are essential to safeguard data against various threats.
- Software Updates: Regular software updates are necessary to maintain system functionality, address bugs, and incorporate new features.
Performance Evaluation
Evaluating CRM performance is critical for determining the system’s effectiveness. Key metrics include:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Customer Satisfaction | Measures the overall satisfaction of customers with the services provided by the tour operator. |
| Lead Conversion Rate | Measures the percentage of leads that are converted into paying customers. |
| Sales Cycle Length | Tracks the average time it takes to close a sale. |
| Customer Retention Rate | Measures the percentage of customers who remain loyal to the tour operator over time. |
| Operational Efficiency | Measures how effectively the CRM system streamlines business processes and reduces manual tasks. |
Implementation Strategies
Successful CRM implementation strategies often involve phased rollouts, pilot programs, and ongoing staff training. A clear communication plan is also essential. Examples include gradual integration of CRM functionality, pilot programs in specific departments, and providing regular training sessions.
Step-by-Step CRM Setup Guide
- Needs Assessment: Identify specific business needs and goals for the CRM.
- Selection: Research and choose a suitable CRM system.
- Data Migration: Migrate existing data into the CRM system.
- Configuration: Configure the CRM system to match the business workflows.
- Training: Train staff on the CRM system usage.
- Deployment: Deploy the CRM system to the entire team.
- Monitoring: Monitor the system and gather feedback for improvements.
CRM for Specific Tour Operator Needs
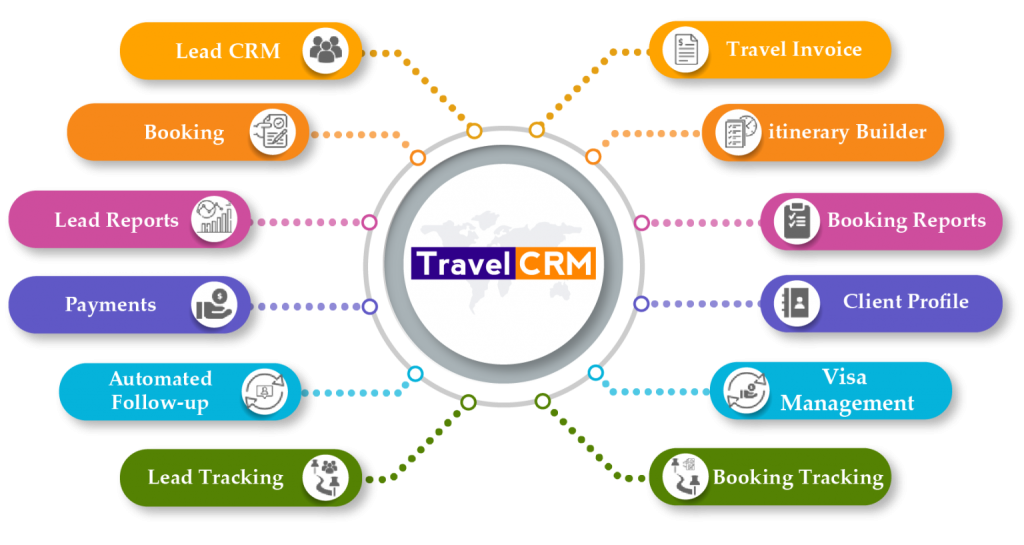
A robust CRM system should adapt to the diverse needs of tour operators, from small, independent businesses to large, multinational corporations. This tailoring involves understanding the specific operational workflows and prioritizing the features that drive efficiency and profitability. Different tour operators have varying requirements in terms of booking management, agent relationships, and staff coordination, necessitating customized CRM solutions.
Tailoring CRMs for specific tour operator needs ensures optimal functionality and user experience. This customization allows operators to leverage CRM features that directly address their business challenges and support their growth strategies.
Tailoring for Small Businesses
Small tour operators often prioritize simplicity and affordability in their CRM choices. The system should be user-friendly, with minimal training requirements, and offer basic functionalities for booking management, client communication, and financial tracking. Integration with existing accounting software is crucial to streamline operations and avoid data duplication. Crucially, the system should scale with the business, accommodating future growth without requiring significant investment in upgrading.
Tailoring for Large Corporations
Large tour operators require sophisticated CRM solutions that can manage extensive data, handle numerous bookings, and facilitate complex operational workflows. These systems typically need advanced reporting and analytics capabilities to track performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. Scalability, robust security measures, and seamless integration with existing enterprise systems are critical factors.
Group Booking Management
Effective group booking management is vital for many tour operators. CRM systems with dedicated group booking modules can handle complex requests, track group sizes, accommodate special needs, and ensure seamless communication with group leaders. Features for managing group payments, confirmations, and itineraries are also essential. Detailed reports on group booking trends and performance can provide valuable insights.
Managing Travel Agents and Wholesalers
Tour operators often collaborate with travel agents or wholesalers. CRMs can facilitate the management of these relationships by providing tools for tracking agent commissions, managing agent contracts, and coordinating bookings. A centralized platform for communication and information sharing is crucial for smooth operations. Tools for handling agent inquiries, feedback, and performance evaluations can strengthen partnerships and enhance overall service.
Managing Tour Guides and Personnel
Managing tour guides, drivers, and other personnel is a key aspect of tour operations. CRMs can streamline this process by allowing operators to track employee schedules, manage availability, and assign personnel to specific tours. Integrated communication tools allow for efficient coordination and quick responses to any issues that arise. The system can also track employee performance and provide opportunities for feedback and development.
Custom CRM Functionalities
Many tour operators benefit from custom functionalities tailored to their specific needs. For example, a tour operator specializing in adventure tours might need a CRM with specialized modules for equipment management, safety protocols, and risk assessments. A luxury tour operator might need features for managing high-end client preferences, bespoke itineraries, and VIP services. These customized features enhance operational efficiency and provide a competitive edge.
Comparison of CRM Features for Small and Large Tour Operators
| Feature | Small Tour Operator | Large Tour Operator |
|---|---|---|
| Booking Management | Basic booking entry, client details | Complex booking workflows, advanced reporting |
| Agent Management | Basic agent commission tracking | Advanced agent management, performance analysis |
| Staff Management | Basic staff scheduling, contact details | Detailed staff scheduling, performance tracking |
| Reporting and Analytics | Basic reports on bookings and sales | Advanced analytics, data visualization |
| Scalability | Essential for future growth | Critical for managing extensive operations |
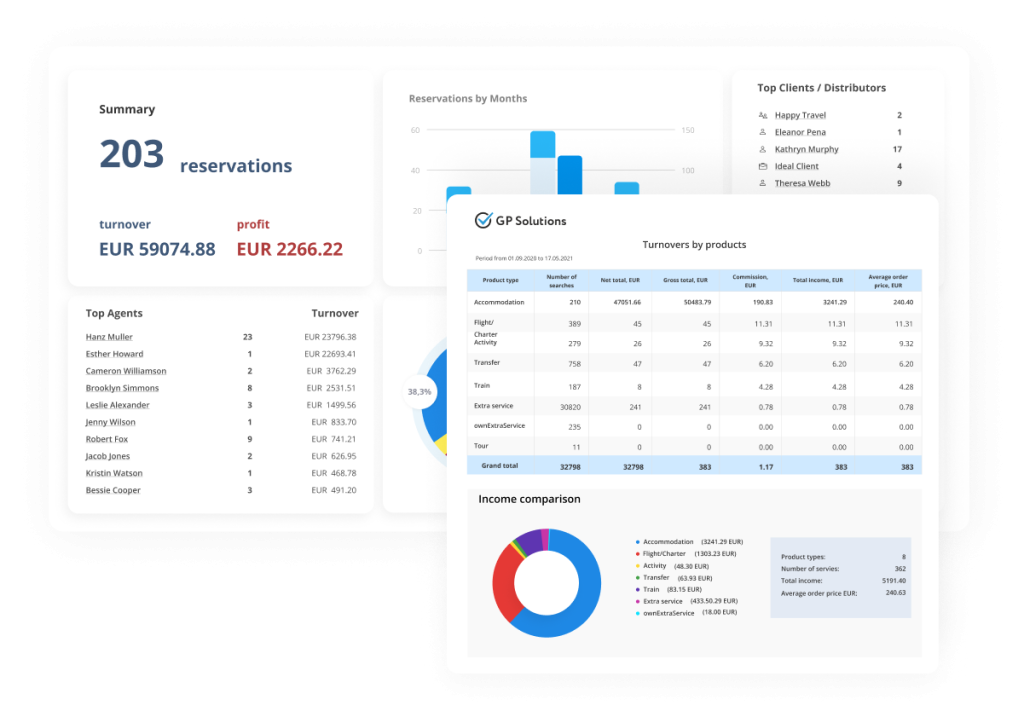
Data Management and Reporting in CRM
A robust CRM system for tour operators is crucial for effectively managing customer interactions, sales data, and operational information. Proper data management within the CRM empowers operators to gain valuable insights, optimize their offerings, and enhance the overall customer experience. Effective reporting mechanisms are essential for tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), identifying trends, and making data-driven business decisions.
A well-structured CRM system streamlines the process of collecting, organizing, and storing customer data. This structured approach enables tour operators to access crucial information quickly and easily, facilitating personalized service and targeted marketing campaigns. This efficient data management process fosters stronger customer relationships and enhances the overall operational efficiency of the business.
Effective Customer Data Management
Tour operator CRMs facilitate effective customer data management by centralizing all relevant information in a single platform. This centralized approach ensures that all departments have access to the same up-to-date data, minimizing inconsistencies and maximizing operational efficiency. Comprehensive customer profiles are created, encompassing details like booking history, preferences, and communication preferences. This enables targeted marketing campaigns and personalized service, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Data Security and Privacy Considerations
Ensuring the security and privacy of customer data is paramount in a tour operator CRM. Robust security measures, such as encryption and access controls, should be implemented to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access. Compliance with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, is crucial. Regular security audits and employee training on data protection protocols are essential to maintain a secure environment.
Generating Performance Reports
CRM data can be leveraged to generate a variety of reports that provide valuable insights into tour operator performance. Sales reports can track revenue generated from different tours, destinations, or booking channels. Marketing reports can assess the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and identify high-performing channels. Operational reports can monitor the efficiency of internal processes, such as tour preparation and customer service.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Tour Operators
Identifying and tracking relevant KPIs is essential for evaluating CRM performance and business success. Key metrics include customer acquisition cost (CAC), customer lifetime value (CLTV), average order value (AOV), conversion rates, and customer satisfaction scores (CSAT). These KPIs provide a comprehensive view of business performance and enable data-driven decision-making. For example, a high CLTV indicates a strong customer base, while a low CAC suggests efficient marketing strategies.
Importance of Data Analysis for Strategic Decisions
Data analysis is critical for making strategic business decisions in the tour operator industry. Analyzing CRM data helps identify emerging trends and patterns in customer behavior, market demand, and competitor activities. These insights can be used to develop new products, improve existing services, and optimize pricing strategies. For example, analyzing booking patterns can reveal seasonal demand fluctuations, which can inform inventory management and marketing strategies.
Potential CRM Data Trends and Patterns
CRM data can reveal insightful trends and patterns, such as increasing demand for eco-tourism tours, rising popularity of specific destinations, or the preferred booking channels of target customer segments. Analyzing these trends helps tour operators adapt to evolving customer preferences and market demands. For instance, a significant increase in bookings for a specific tour type might suggest a new market opportunity or the need to expand existing offerings. Historical data analysis can reveal patterns in customer behavior, such as the tendency of certain customer segments to book tours during specific months or seasons.
Outcome Summary: Tour Operator Crm
In conclusion, a tour operator CRM is a powerful asset for any tour business, regardless of size or specialization. By effectively managing customer relationships, streamlining operations, and fostering personalized experiences, a well-implemented CRM can significantly contribute to the success of a tour operator. Understanding the various aspects of CRM functionality, integration, implementation, and data management is crucial for achieving maximum return on investment. The tailored approach to specific needs, be it small business or large corporation, ensures optimal efficiency and profitability. Ultimately, embracing a tour operator CRM is an investment in long-term success and customer satisfaction.